Sales management can be associated with working with reports, analysis and CRM system administration. However, it is only a small part of the duties of a good sales director as the truth is he should spend 20 percent of his time in numbers and invest the rest of his resources in working with the team.
Building a dedicated and effective sales team is a challenge. The sales team works under pressure of performance all month. In a well-managed department, a group of individuals of different characters work on the basis of one sales process, jointly achieving the goals set by the company.
The sales team is just like a football team. Footballers require constant training and activity to stay in shape. They must properly manage their health and fitness to always be fully available during the match. A salesman must maintain a good performance, keep his product knowledge up to date, and all this managing the activities related with the sales funnel to fulfill the plan.
So how to effectively manage the sales department.
1. Sales process and guidelines
You will find an exhaustive article on this subject in the previous entry.
The sales process is the basis of the team structure. You should employ and expand the team in the company according to the process you’re using. As InStream Group, we are the authors of an innovative method of building and planning the sales process. We call it a sales process matrix.
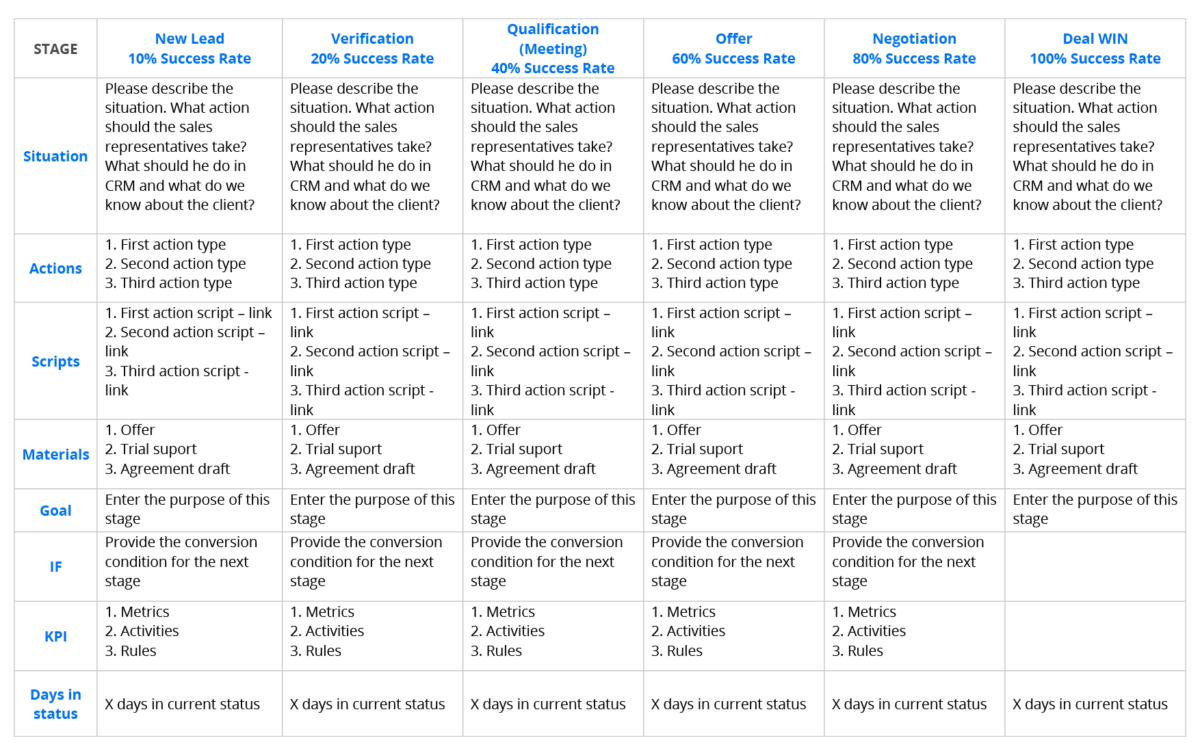
As I have already mentioned, you will find more details about working with the sales process matrix in the above attached link to the article.
The development of the sales process allows you to plan frameworks and employ people with the right competencies for the proper functioning of the team. However, the implementation of a structured sales process is not as simple as it may seem from this brief description.
The roles of the sales process in the company:
- structuring of activities, which facilitates measurement of performance;
- the possibility of mapping the process in CRM;
- quick implementation of new team members into the process;
- easy measurement of salespeople’s effectiveness at various sales stages;
- measuring Lead to SQL, Lead to Opportunity, Lead to Offer, Lead to Deal.
- scaling the team based on real needs resulting from the process;
- standardizing customer communication within the process.
Before creating a sales structure, you need to plan the first stage of work: the process.
2. Sales environment and culture
Before a sales team takes shape in the company, it is also necessary to consider whether the company has an appropriate sales culture and technological environment to support the envisaged process.
A sales culture is composed of elements such as: process, communication, work rules and environment. Unfortunately, many companies employ salespeople and expect a lot from them, but do not provide them with appropriate conditions. In such a situation a salesman is a bit like a football player without training, good shoes and a healthy diet. Left on his own, he will lose his motivation, it will be difficult to assess his real possibilities and, as it is usually the case, he will not sell.
Therefore, the next step after implementing the process should be to plan the rules of work in the sales department and then make sure that these rules are clear and known to everyone.
The second equally important item is to design an appropriate environment, namely sales support tools. The more they are suited for your business, the better the results they bring.
CRM system is, of course, one of the basic tools. It is very important to map the process in the CRM system and enable the team to carry out activities in accordance with the sales process matrix. Thanks to this, CRM will not only be a base of contacts but a proper tool to manage sales in the company.

3. Sales organization structure
Many companies are still based on a flat sales organization structure. This means that every salesman is responsible for the whole sales funnel: is involved in lead sourcing, sales activities and, on top of that, customer service activities.
We advise against such a structure. There are certainly better solutions.
One of them is to design the process so as to create different specialties at different stages of the sales funnel.
Below is an example of a sales organization structure that takes into account the structure of a department with Pre-Sales and Sales specializations.

The design of the sales department in such a way allows to distinguish 3 specialised teams:
– Pre-Sales: lead acquisition and lead qualification department, that is LEAD to SQL conversion;
– Sales Development: sales department responsible for closing contracts, i.e. SQL to Deal conversion ;
– KAM: (Key Account Manager) current customer service department: cross-sell, upsell, maintenance.
A sales organization structure designed in this way has many advantages over the flat one:
- everyone is responsible for a specific part of the process and the roles are easy to determine;
- 100% of the salesman’s potential is used;
- it is possible to select a team of “Hunters” and “Farmers” business representatives;
- it is easier to develop and measure the performance of the department, and thus to scale it further.
Thanks to a transparent structure, you are able to efficiently recruit and fill new positions. As a manager, you can select the candidates according to the different needs of each particular position. For example, a Pre-Sales business representative is a person who should like to establish and maintain relationships with customers. KAM employee would be a typical farmer who works on the already built potential and needs completely different qualities.
4. Remuneration system
The bonus program is of course a key element in managing and motivating team members. There are many models and it is difficult to determine which one is most effective. Bonus programs most often depend on the prices of services and products sold as well as the sales cycle—whether it is a monthly, quarterly or annual one.
Some basic rules concerning the bonus program:
– It must be 100% dependent on the employee and his or her effectiveness, not on team performance;
– The team bonus should be calculated as a separate KPI and motivation factor;
– It must be clear, easy to calculate;
– It must be achievable and motivating (goals set too high tend to demotivate the team);
– It must always be discussed with the team and properly justified.
Bonus program model—% of sales
This is the simplest bonus program model. It consists in giving the employee a bonus in a certain percentage of the income realised by him.
A salesman who will raise PLN 10,000 for the company, with a 5% of bonus commission program, will receive PLN 500.
Companies use gross/net income here, depending on product margins.
This model is most often used for quarterly or annual sales cycles, where sales are less frequent but where their volumes are larger.
Bonus program model—fixed amount for plan implementation
Another bonus program model envisages paying the employee a certain amount once 100 % of the plan has been implemented.
In such a model, a salesman will receive e.g. PLN 500 of a fixed commission only when he realizes PLN 10,000, that is 100% of the plan. If he realizes PLN 8,000, which represents 80% of the plan, he will receive PLN 400 etc.
This solution is used in short (monthly and quarterly) sales cycles.
Bonus program model – % of the sales dependent on the stage of plan implementation
This model is a combination of the two previous models. In this case, you first specify the % of the bonus commission which is paid to the salesman for completing the 100% of the plan.
100% of the plan—5% of the bonus commission
80% of the plan—4% of the bonus commission
60% of the plan—3% of the bonus commission
50% of the plan—no commission
The commission system must not only serve the needs of the company, but also be a motivator for the team.

5. Bonuses, awards
The sales team needs different motivations. Throughout the whole year, every month, the sales team should work with a specific goal in mind. That’s why the constant presence of possible awards on top of the plans and commissions means better motivation and healthy competition within the team.
Here are some examples:
– a bonus for implementing 50% of the plan by the 10th day of the month;
– a bonus for selling a specific service;
– a bonus for selling products/services with a certain margin;
– a bonus for keeping sales at a certain level during the quarter;
– annual bonus;
– team bonus.
Bonuses are a very good tool to control the portfolio of services sold. If a company has a need to increase the sales of specific services, bonuses can play key roles here.

6. KPI
We wrote about what to measure and what is important for the sales department in the previous set of articles. In order not to overlap with what you already know of the KPIs, here let’s focus only on some of their key aspects.
It is important that KPIs play a real role in managing the sales team, KPIs are not just secondary data.
One of the interesting ideas is basing basic bonuses on KPIs.
Assuming that the base of a salesman’s salary is PLN 5,000 net, it can be established that this amount consists of PLN 4,000 net base and PLN 1,000 bonus (not to be confused with commission). If a given salesman in a particular sales cycle (month, quarter) realizes X>80% of a plan, the bonus is automatically included in the base + he also obviously receives commissions according to the plan.
However, if a salesman performs less than 80% of the plan, the KPIs are used to calculate the amount due from the PLN 1,000 bonus. As an example, let’s see some factors that could be taken into account:
- number of outgoing calls made;
- amount of time spent on calls;
- number of meetings;
- quality of work in CRM (Lead Service).
If the KPIs are not met, the employee will not receive a full bonus of PLN 1,000.
The last key element is a committed sales director. Working with the team should consist of spending 80% with people and 20% with the data. The director should not retreat into numbers, but should be an example of a leader who guides the team and is involved in sales processes.



